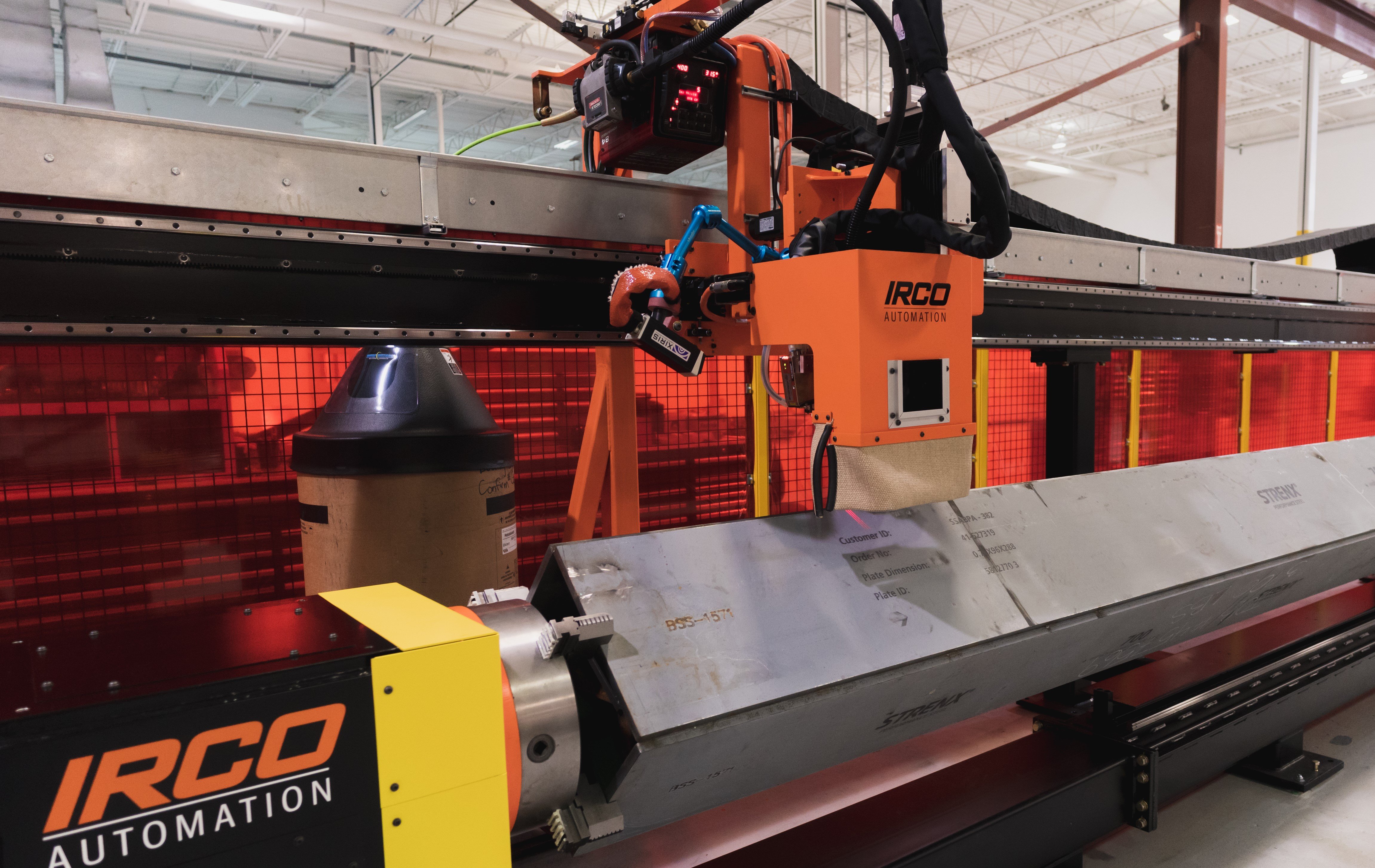
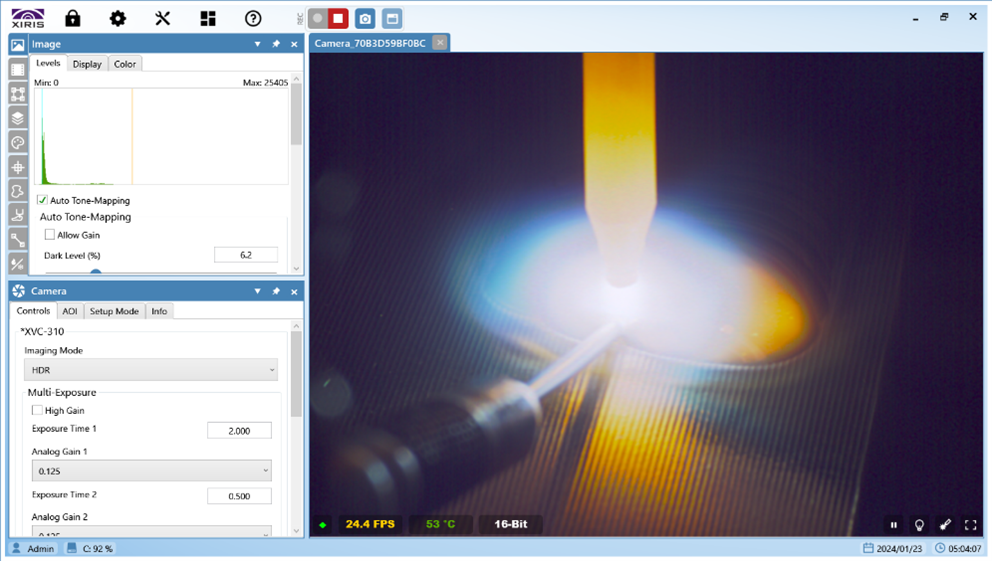
Hypodermic needles are usually made by drawing down small-diameter stainless steel tubing that has been welded on a miniature tube mill using a tungsten inert gas (TIG) or laser welding process. After welding, the tube is drawn through progressively smaller dies to size the needle.
On a welded needle tube, welding defects occur that are similar in nature to what might occur in larger, thicker walled tubing. These defects include:
- Mismatch (uneven joining of two halves of the tube material).
- Raised/sunken welds (height of the center of the bead after welding relative to the parent material—severe cases become pinholes).
- Bead width (width from edge to edge across the bead).
- Forming deflection (deflection of the formed tube from an ideal circle).
In order to detect these common defects on an object of consideration as small as a needle tube, a highly precise laser measurement system is required.
To measure the weld properties and identify possible defects related to the weld bead on welded needle tubes, Xiris developed an Ultra High Resolution version of its laser-based 3D Inspection system, the WI2000p. This system is implemented on a needle tube mill producing 3 mm diameter tubing using a TIG welding process. The inspection system has a measurement resolution of approximately 0.003 mm per pixel and a field of view of about 2 mm x 1 mm.
The inspection system is placed after the weld head about 25 mm (1”) off the tube. Whenever any defects are detected, an output signal is sent to the mill’s programmable logic controller (PLC) to notify the operators of a defect on the tube. The defective tube is then marked or quarantined for further testing.
Sample Images and Data
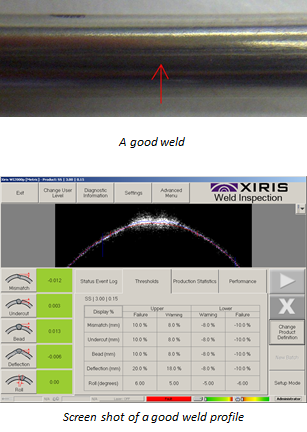
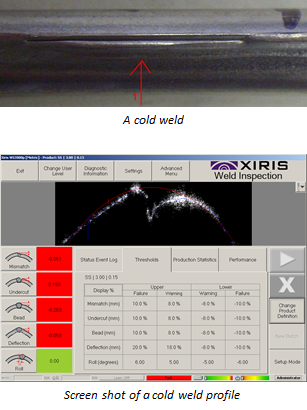
The screen shots of the laser inspection system show a critical variation in the undercut or bead measurements at selected points along the length of the weld, indicating defects present on the needle tube. These defects may contribute to a weakened seam and potential product failures in the field. In addition, other potential defects such as mismatch or forming deflection at the point of welding can be detected, helping the operator in calibrating the mill operation.
Conclusion
To achieve adequate weld process quality control, fabricators of needle tubes require a very accurate laser measurement system that’s capable of reliably detecting weld defects on such a small workpiece during the milling process.