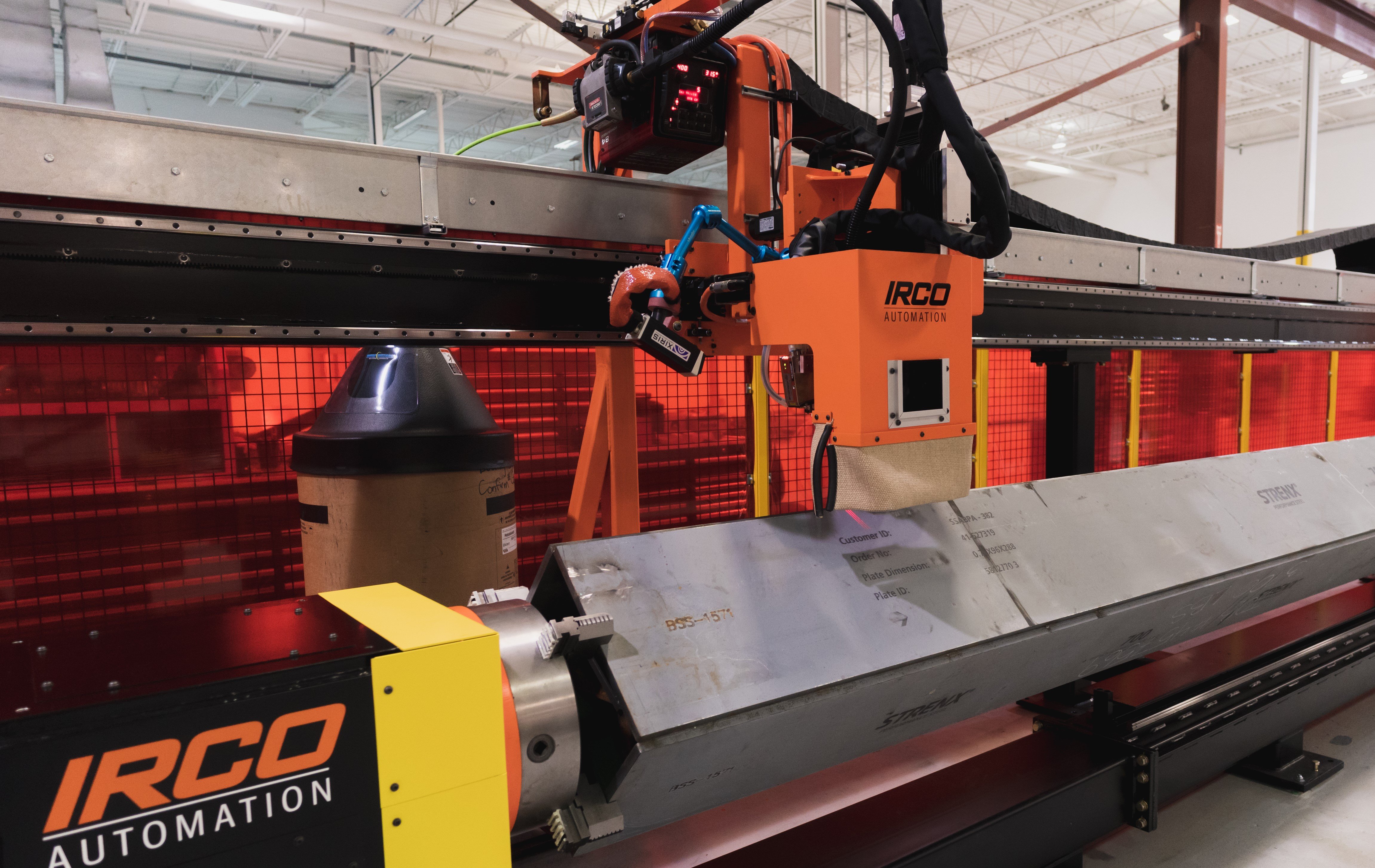
Highly precise welding procedures commonly found in power generation applications where thick walled sections of pipe are welded together using multi-pass TIG welding procedures have demanding quality monitoring requirements. One of the most important monitoring tasks is to monitor the quality of the melt pool from the back side of the weld. In the case of orbital welding two sections of pipe together, this is often done by using a Xiris weld camera mounted inside the pipe looking at the backside of the root pass of an orbital welding head operating from the outside of the pipe.
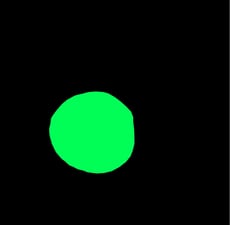
If a Xiris weld camera is mounted inside the pipe looking at the melt pool, what is visible is a high intensity spot surrounded by an area of lower intensity (see Figure 1 below). Precision fabricators are often interested in the shape, size and location of the precise boundary of the melt pool relative to the weld seam. Segmentation of the edge of the melt pool is therefore an important first step to measure the shape of the melt pool.
Xiris was given this task to first detect the edges of the melt pool, then measure the size, various shape parameters, and the center of the object relative to the weld seam.
 |
|
 |
|
Fig. 1: Original Image of Melt Pool |
|
Fig. 2 Segmented Region of Interest |
Once the Melt Pool can be correctly segmented from the rest of the image, the Xiris Blob Analysis tool can be used to compute various measurements of the region of interest, such as; centroid, area, perimeter, bounding box, and roundness, that together, provide information such as; to how well the melt pool is forming, if the welding torch is burning through, if the weld torch is tracking the seam properly and other process features.
Image processing tools, like Blob Analysis, can be used to find valuable shape, size and location information of key features of the welding process. When combined with a Xiris weld camera, real time analysis can be achieved.
Follow Xiris on social media for regular updates and welding videos!


.png)

.png)
