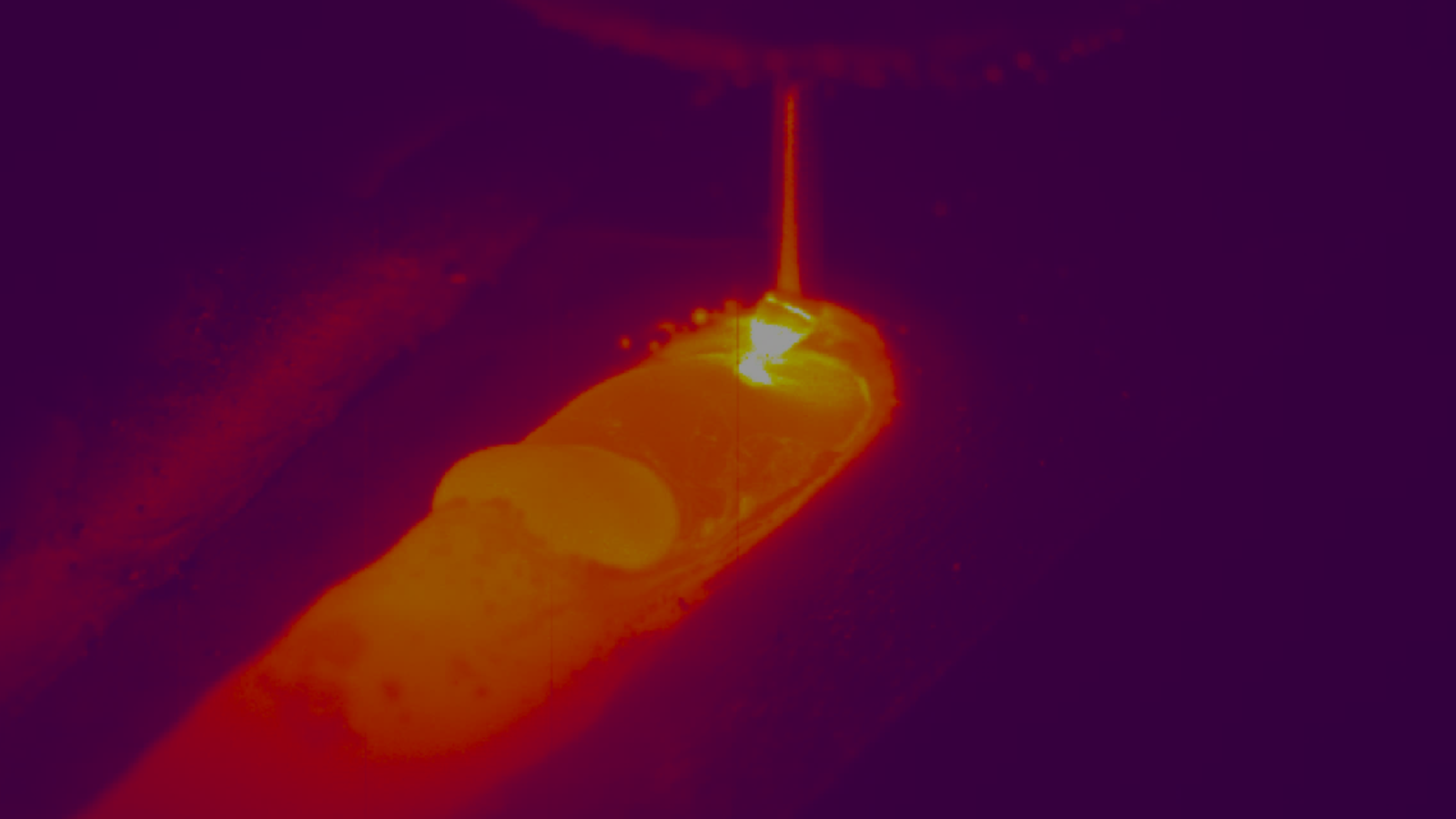
Additive Manufacturing refers to a process whereby 3D design data is used to build up a component by depositing successive layers of material to create the shape required. It is also referred to as "3D printing" and can be used to create almost any shape or geometry that is generated from a 3D CAD model. It is called Additive Manufacturing because material is added together to form a part, distinguished from conventional manufacturing where material is removed to form a part.

Instead, Xiris Weld Cameras can be used to record the process to produce crisp and clear images of the weld head, laser spot, melt pool and weld bead. The result is a video of the process in stunning high resolution and clarity, at rates that can exceed 200 frames/sec. This can allow engineers and scientists to monitor the process live and stop right when an error occurs. Or, the recorded video can then be played back at a higher speed to allow engineers and scientists to review the process from start to finish and carefully review the events of greatest interest at a lower speed, as required. This allows the R&D team to focus on the time of welding defects and errors, by finding out exactly what went wrong with the process by analyzing the recorded video at the time of interest.

Conclusion
The development effort to improve an additive manufacturing process can be long and tedious. Using a Weld camera to monitor the process can both help to reduce the labor required to improve the process but also provide better documentation and highlighting of the process variations as they occur.
For more information on how Xiris Weld Cameras can help with your Additive Manfacturing applications, visit Xiris.com


.png)

.png)