Welding is often referred to as “industrial craftsmanship”, a term that is justified given the detailed process involved in combining metals through a complex interaction of electricity, heat, melting, mixing, and solidification. In most cases, welding is done to achieve smooth metal joints that are both reliable and visually appealing. From bridges and airplanes to pipes, medical devices, and beyond, welding remains a ubiquitous technology in achieving remarkable results across various industries. Even though welding is used to join some of the most precisely engineered infrastructures in the world, its techniques and practices remain variable and inconsistent. Even though large-scale welding applications are becoming more and more automated, manual welding still prevails in many applications depending on the expertise and skills of a welder. Either way, the process depends on weld parameters that were validated many years ago.
No matter the number of studies conducted on its methods and practices, welding still falls short of expectations. This shortfall is because of the lack of datasets needed to create a framework that can help welding elevate to a science rather than just a craft. Collecting process data is the only way to enhance welding best practices and ultimately establish standardized protocols.
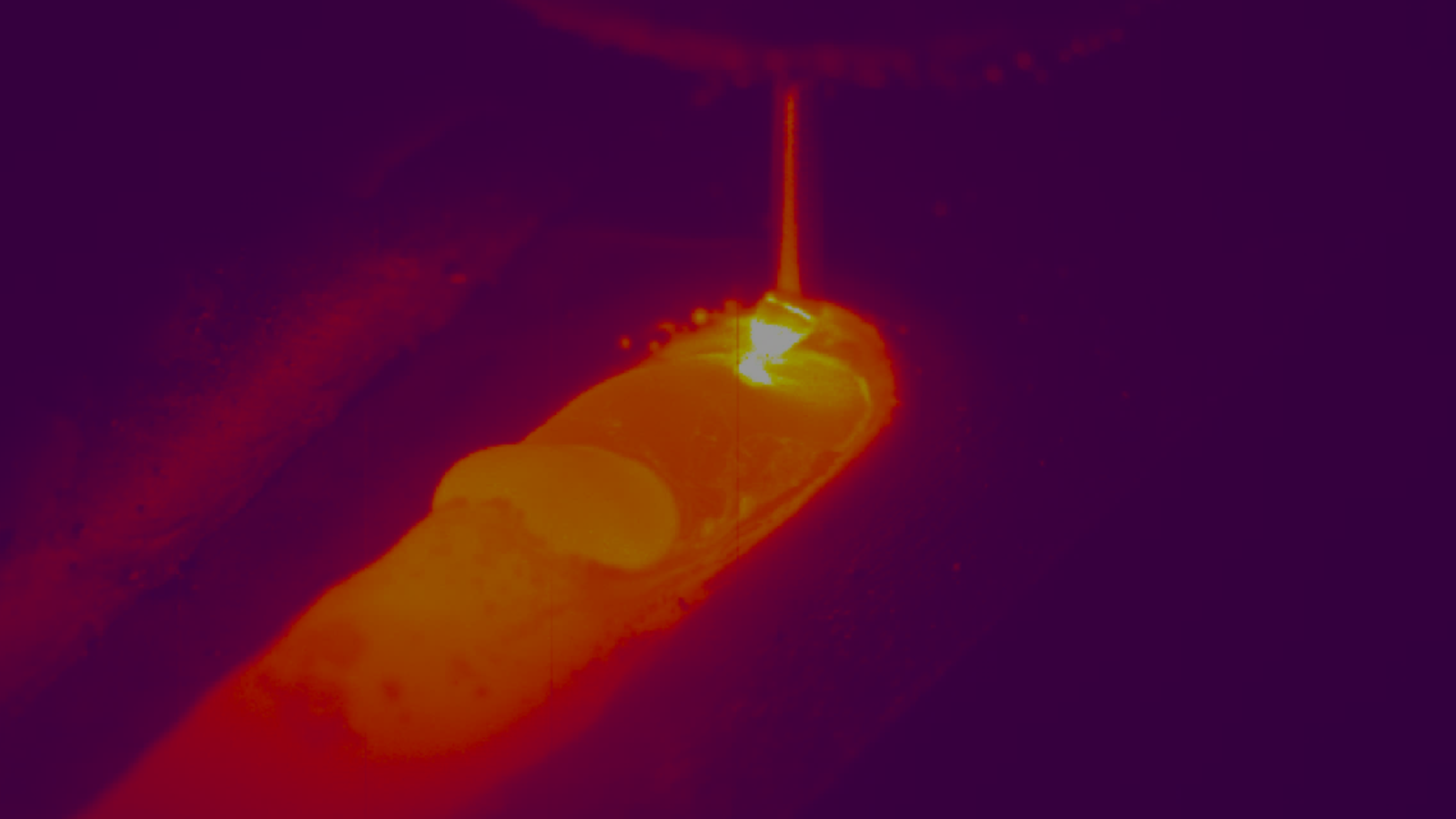
.png?width=866&height=440&name=Fig.%201%20A%20screenshot%20from%20Xiris%20Weldstudio%20Showing%20Blob%20Data%20of%20Melt%20Pool%20(Xiris).png)
Fig. 1: A Screenshot from Xiris’ WeldStudio Showing Blob Data of Melt Pool (Xiris)
|
Understanding Weld Process Data
Welding a metal joint involves melting a filler material into the gap to create a structurally sound assembly. Over time, numerous carefully assessed variables have been introduced to the welding industry, all incorporated to enhance welding outcomes. These factors are variable and might change pre-weld, during welding, and post-weld. Process data helps in maintaining specific settings about the weld material and the weld process and can help facilitate conducting comparisons and continuous improvements.
Owing to advances in sensor technology, data collection has become more achievable and appealing in challenging environments such as welding where safety from environmental hazards from fumes, gases, radiation, sparks, noise, and fire are paramount. For welding processes, there are many sensors, for example, thermal sensors or cameras to record heat distribution in the weld; thermal cameras to detect the temperature of the melt pool and its surrounding area, Gas Sensors can analyze the composition of shielding gasses used, voltage and current sensors can provide real-time electrical data of the power supply, and velocimeters can measure the feed speed of the filler wire. All this data can then be collected and analyzed to provide feedback on many of the welding parameters.
Welding process data can have a significant impact on the quality and formation of a weld. In automated processes, the sensor data enables easy and quick optimization of the welding parameters providing a balance between factors like production speed and quality. In orbital or other precision welding processes, detailed data analysis can help to ensure high-quality welds with minimal chance of defects in the weld.
Other than serving to enhance weld quality, weld process data can also help to contribute to advancements in welding technology. Technicians, researchers, students, and industry experts can all gain insights into weld process information that extends beyond immediate production goals.
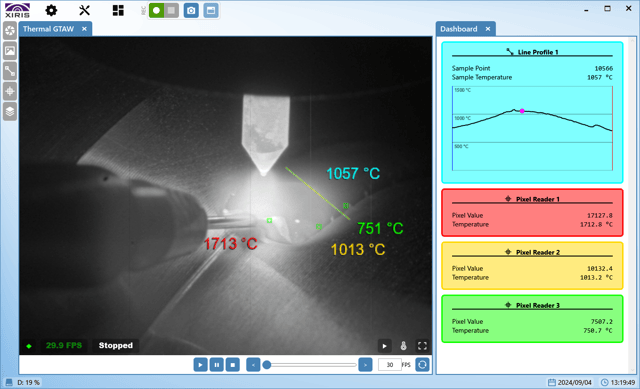
Fig. 2: A Thermal Image of a GTAW Process with Temperature Measurement Tools (Xiris)
|
Significance of Analyzing Welding Data
Analysis of weld process data across different types of welding and materials helps in de-cyphering crucial insights into the weld process such as how weld parts are functioning as per expectation, the need for change and improvement, and what else can be done to enhance quality. All these discussions lead to the thoroughness of weld-data recording and analysis.
The many benefits of weld process data go beyond just improving quality, but can also enhance:
- Safety: The constant record-keeping of weld data helps to validate welding parameters to indicate if a process is followed with best practices for safety, such as the application-specific voltage and current limits, the rate of gas flow, air quality standards, environmental factors, temperature guidance, best usage patterns, and others.
- Maintenance: Weld process data records of equipment calibrations and results can help in the early detection of equipment malfunction by following the trail of numbers and data. Regular and scheduled maintenance will ultimately result in more consistent welding results.
- Productivity: Weld data collection ultimately leads to making changes in the ongoing process, to change and check possible constrictions in production and manufacturing. The result is a quick and proven way to improve the quality of the end product, setting standards and improving productivity. It enables proper usage of resources and time.
For individual welding processes or small-scale production, collecting weld process data may initially seem unnecessary or overly difficult. However, considering the impact that data collection can have on overall annual production makes it essential for achieving operational efficiency and growth. Benefits such as those listed above stand true for every welding process no matter the value of the end product and scale of the process. Data-driven results help in selecting appropriate material and following proper welding protocols and can also be used for education purposes to train or educate new welders.
A highly skilled welder is difficult to find owing to the physical aspect of the process, however, following a pattern of numbers to attain specific outcomes is comparatively easy and is more appealing to the current workforce. With advances in the fields of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, automation, and robotics, there are many new opportunities to significantly advance the welding processes.
Ease of Weld Data Collection and Analysis Using Xiris Vision Systems
Xiris takes pride in our vision systems by producing products that help improve the overall welding process through advanced technology. Here’s how:
- High-Quality Imaging: Our high-resolution, high-dynamic range cameras are designed to work in harsh welding environments with smoke, heat, and bright light from an open arc welding process. Our weld cameras can seamlessly capture the real-time welding process. See: Xiris Weld Monitoring Cameras
- Automatic Inspection System: Along with continuously monitoring the weld with a camera, machine vision processing can be used to extract information about the process to automatically determine the ongoing process of welding. Automatically detecting certain weld defects and process anomalies becomes possible, which when fed back to the automatic welding equipment can enable quick process adjustments to correct the issue. See Xiris Machine Vision Systems.
- Data Collection: Xiris’ camera software utility, WeldStudio™, seamlessly connects to all Xiris products, serving as an intuitive interface that provides camera controls, video recording and playback, machine vision algorithms, and a wide array of data collection functionality. Data that can be collected includes shape, size, position, and temperature data of various weld features such as the melt pool, seam position, filler wire, torch tip, and weld bead to generate customized weld quality metrics for any welding process. See WeldStudio™ for more info.
- Analysis and Reporting: Data Analytics tools such as Statistical Process Control (SPC) apply statistical methods to the inspection data reported from WeldStudio™ to monitor and control the characteristics of a welding process. This helps ensure that the weld process will operate efficiently, producing more products that conform to specifications with less waste.
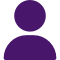
.png?width=800&height=432&name=Fig.%203%20A%20GTAW%20Process%20with%20Various%20Machine%20Vision%20Tools%20Collecting%20Process%20Data%20(Xiris).png)
Fig. 3: A GTAW Process with Various Machine Vision Tools Collecting Process Data (Xiris)
|
Summary
New advancements in welding processes hinge on improvements in quality control driven in part by data collection and analysis. New sensor technologies have made automatic data collection a much easier task in the welding industry, where manual data collection is nearly impossible. For the industry to continue to advance, quality control is of utmost priority, of which data collection is a critical component. Xiris provides a range of real-time weld monitoring and inspection systems with a proven record of data collection that can enhance operational efficiency and support continuous improvements in the welding field.
Stay up to date by following us on social media or subscribe to our blog!




.png)

.png)