Wire-arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) is a material deposition process that builds up a structure layer-by-layer using a multi-axis motion control system and a wire arc welding process. The thermal stability of the process is often a challenge: the interlayer dwell time in WAAM is often preset before the build-up commences. As a result, the required cooling time is usually calculated empirically; it usually does not account for the heat collected in the deposit from one layer to the next.
 (a) (a) |
(b)
|
|
(c)
|
(d)
|
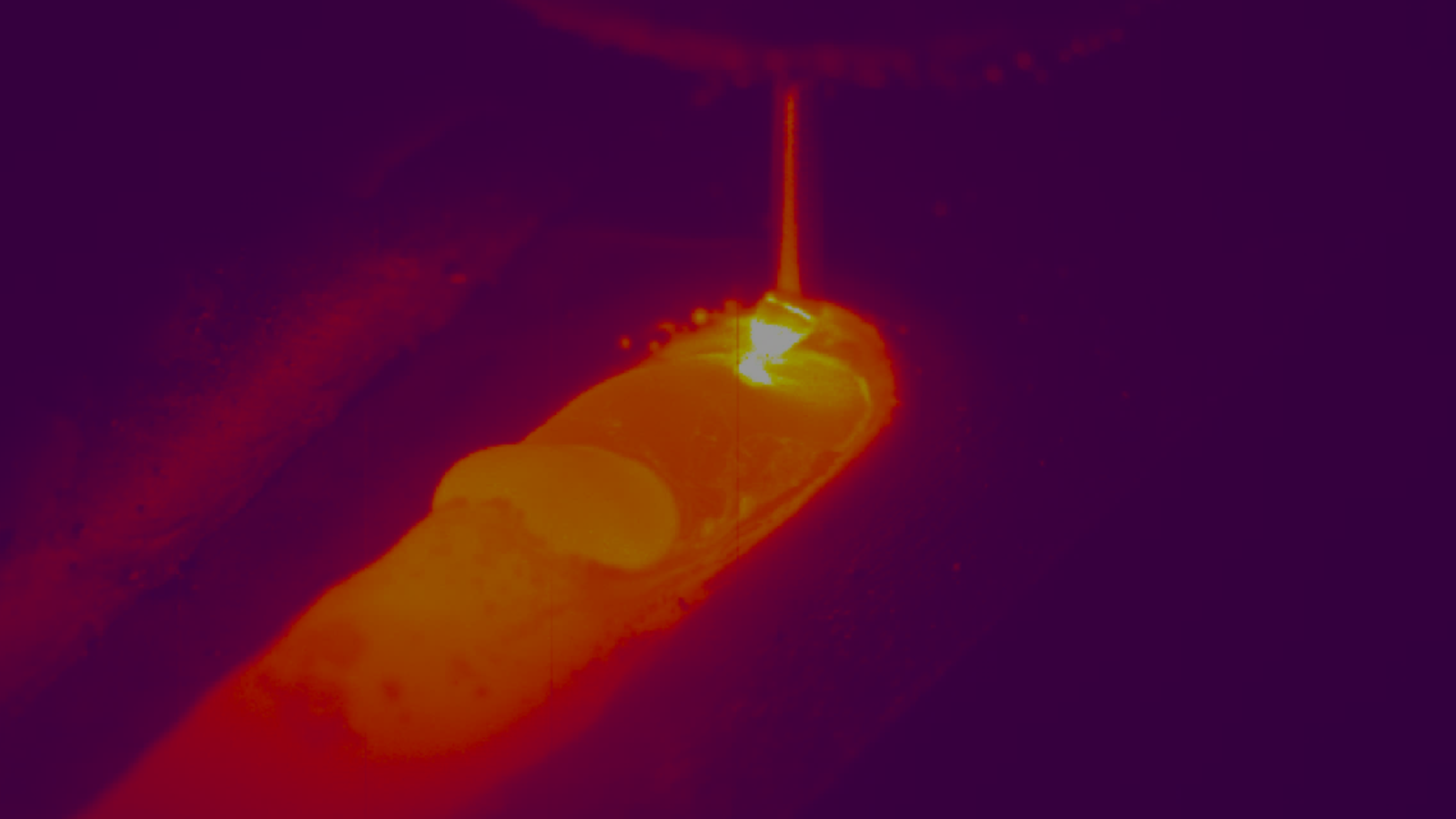
Melt pool parameters (such as area, orientation, width, length, eccentricity, etc.) can be used in real-time to create a closed-loop PID feedback control that will ensure the thermal stability of the WAAM process, ensuring that the required cooling rates are achieved to reach the specified microstructures, particularly when done in conjunction with the temperature measurements from the Xiris XIR-1800 thermal camera. Temperature measurements can improve the closed-loop control by controlling the interlayer temperature: instead of waiting for a preset time between the layers, the camera can measure temperature of each deposited layer and the next pass can be started once the interlayer temperature reaches the necessary value.
Melt pool segmentation can also be used in WAAM processes to make sure that material overflow is not happening by checking that the weld pool size is always within control limits despite heat accumulation. Keeping the heat accumulation within limits can help avoid melt pool collapses that enhance the machining allowance.
Applied together, temperature measurement and cooling rate monitoring provided by Xiris’ XIR-1800 thermal camera and the Meltpool AI tool can offer great control over WAAM processes.
Conclusion
Adaptive Closed-Loop Control plays a significant role in addressing thermal stability challenges in WAAM (Wire-arc Additive Manufacturing) processes. By integrating Adaptive Closed-Loop Control, achieving ideal microstructures in a WAAM process is possible, enhancing thermal stability.
The use of temperature measurements from thermal cameras like the Xiris XIR-1800 can provide additional Adaptive Closed Loop Control options by monitoring interlayer temperature and enabling adjustments to the process in real-time. The result is a process that runs better in control.
Stay up to date by following us on social media or subscribe to our blog!







.png)

.png)