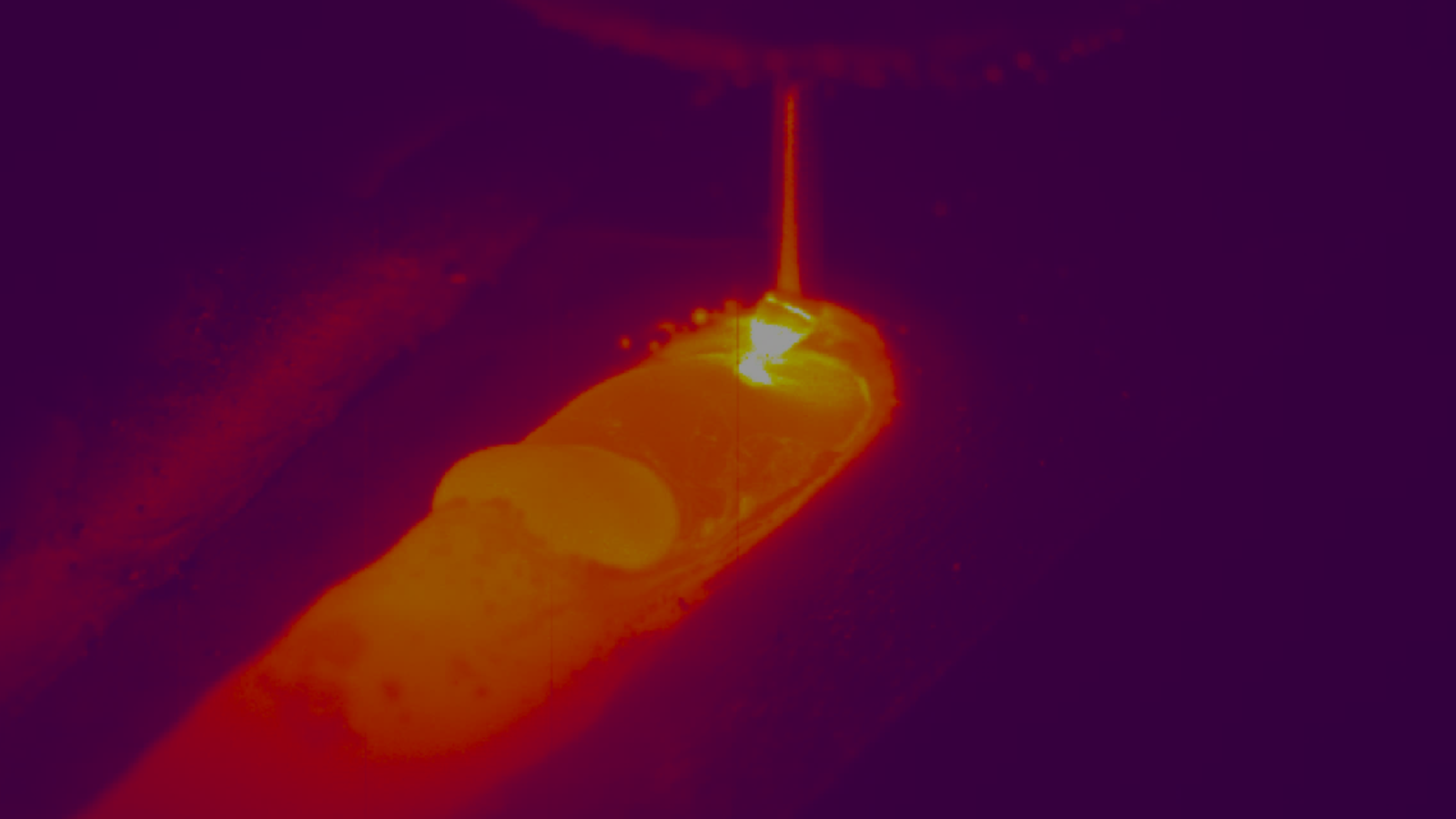
Perforated tubing has a variety of end user markets, particularly with applications in the automotive industry where they are most commonly used in exhaust and filtration assemblies. The tubing starts out as a coil strip pre-perforated with holes that can have almost any perforation shape, pattern, or hole size. The perforated coil strip is usually made by punch press on a separate process and then delivered to the mill for forming into a tube.
 A close-up view of a perforated tube. Image courtesy of www.perforated-tube.com
A close-up view of a perforated tube. Image courtesy of www.perforated-tube.com
When such perforated material is formed into a tube, it often cannot be tested using traditional Ultrasonic or Eddy current processes as they usually require a solid material to transmit the signal and create a suitable signal “signature” that can be analyzed for defects. In the case of either testing technique, the test transducer sends sound or electrical current through the material to be tested. If the material is solid and free from defects, the sound waves or electrical current will pass through the material. In the case of a perforate tube, the sound waves or electrical current will hit the perforations, bounce off them and causing an unpredictable result, rendering the test procedure ineffective.
Instead, using a non-contact laser triangulation method to optically measure the geometric profile of the weld bead and the forming of the tube is the only robust solution for making some of these measurements. Systems such as the Xiris WI-2200 use a laser and can be set-up to easily detect variations in the weld bead profile and/or form of the tube, all while ignoring the presence of perforations in the parent material of the tube.
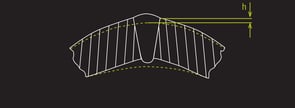
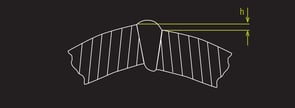 Example of tube defects that laser weld inspection systems such as the WI-2200 can identify.
Example of tube defects that laser weld inspection systems such as the WI-2200 can identify.
Top: Deflection, Bottom: Mismatch
Just like non-perforated tube inspection, defects that can be detected by the laser triangulation system for perforated tube include excessive or sunken bead height, mismatch, deflection, undercut, freeze line and others. To learn more about each of these defects, visit our defect detection blog series, where we discuss various profile defects such as scarf width, deflection, and measurements related to the weld bead.
For more information on our WI-2200 Weld Inspection System, visit our product page or connect with a product expert.
Stay up to date by following us on social media or subscribe to our blog!


.png)

.png)