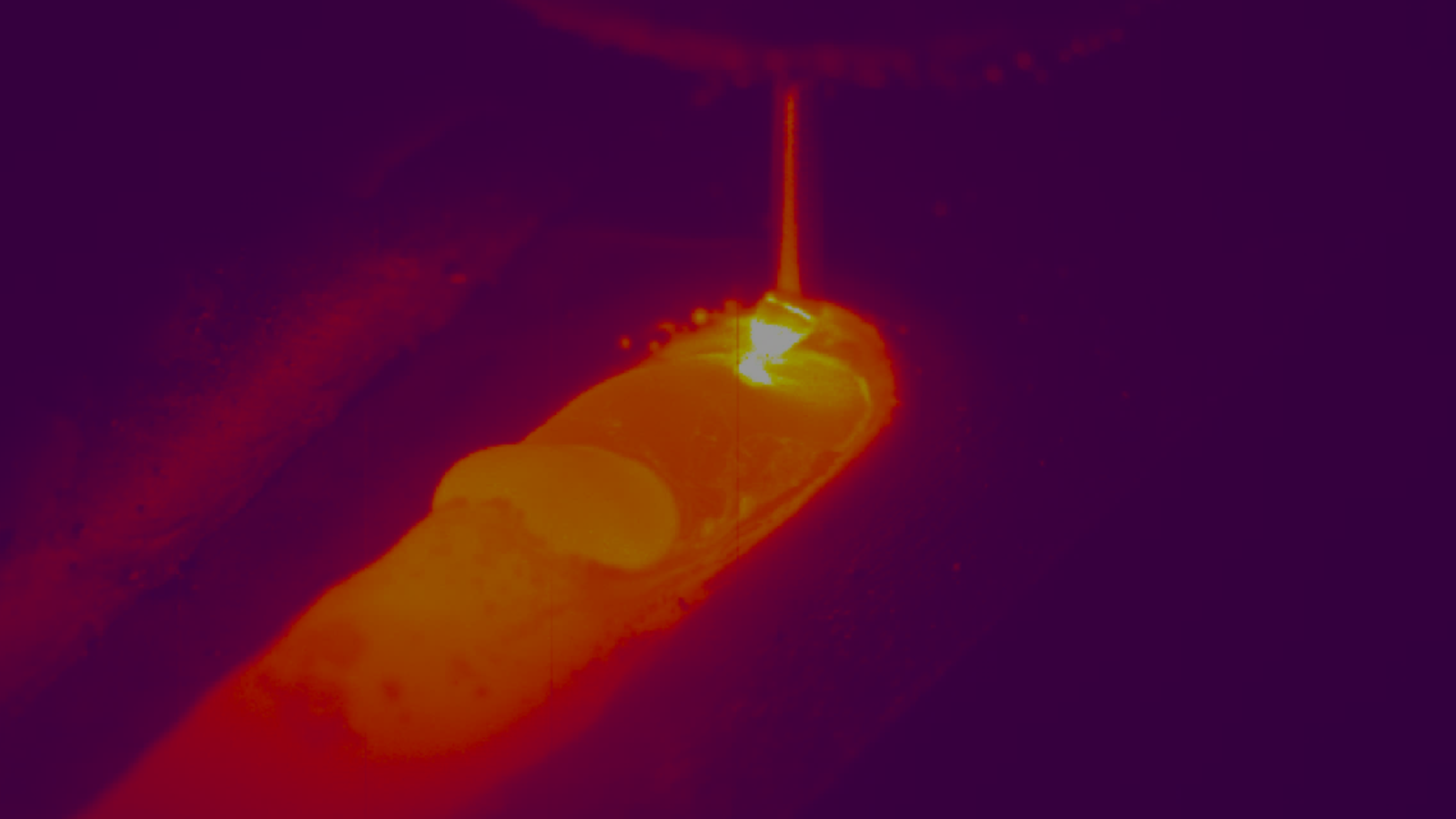
Welding hasn’t always been seen as a data science discipline, but that’s changing fast. As automation, AI, and digital manufacturing reshape industry expectations, welding monitoring is emerging as a crucial enabler of quality, automation, and efficiency.
From academia to industrial adoption, the trajectory is clear: welding monitoring is becoming a strategic necessity. Let’s look at what’s coming next.
1. A Market on the Rise — Real-Time Monitoring Goes Mainstream
According to industry forecasts, the real-time welding monitoring system market is rapidly expanding. In 2025, the global market was estimated at nearly USD 1.76 billion, and analysts expect this to grow to over USD 4.14 billion by 2035, with a CAGR of 8.6 % (Market Growth Reports, 2025).
Key takeaways:
- Real-time data is now essential in automotive, aerospace, oil & gas, and other precision-critical industries (Market Growth Reports, 2025).
- North America leads adoption, but Asia-Pacific is catching up quickly due to manufacturing expansion (Market Growth Reports, 2025).
- Sensor integration with cloud analytics and predictive tools is steadily increasing (Market Growth Reports, 2025).
- This underlines the shift from manual inspection toward continuous digital quality assurance, a foundation for Industry 4.0.

2. AI and Machine Vision
Academic and industry research confirm machine vision isn’t just capturing images — it’s becoming an intelligent sensor suite. Welding monitoring studies show:
In fact, Xiris cameras are already being used in machine vision applications where deep learning models analyze the weld pool, monitor arc stability, and measure heat distribution. With the Xiris WeldStudio™ software, engineers can overlay real-time data, apply blob analysis, or segment the weld pool for AI interpretation, effectively teaching machines how to see weld quality. This transition from visualization to intelligent monitoring is a cornerstone of the next generation of automated welding systems. In other words, weld cameras aren’t just seeing the process, they’re interpreting it and making the data actionable. This trend will accelerate as edge computing and GPU-based analytics become more accessible (Quality Magazine, 2024).
3. AI-Driven Quality Control and Predictive Systems
AI’s role in welding monitoring is rapidly expanding — from parameter adjustment to predictive analytics. Using data captured by thermal and optical cameras, manufacturers are building digital twins of their welding processes, simulating outcomes before they happen (Wikipedia, 2025). The Xiris XIR-1800 SWIR thermal camera, for instance, provides precise temperature mapping of weld pools and heat-affected zones (HAZ), allowing researchers and engineers to measure cooling rates, inter-pass temperatures, and thermal stability during multi-pass welding or additive manufacturing. These insights power predictive quality control, enabling operators to anticipate defects rather than react to them.
4. Robotics + Vision = Smarter Automation
Robotic welding is one of the fastest-growing areas where vision monitoring plays a central role:
For example, manufacturers using Xiris HDR cameras in robotic cells report more consistent bead profiles, reduced spatter, and fewer costly reworks. When combined with thermal monitoring, this technology offers a complete visual and thermal understanding of the welding process, something that was almost impossible just a few years ago. The future of welding is automated but adaptable, human expertise guided by real-time data and machine learning.
5. Education, Research, and Skill Growth
Monitoring technologies are also shaping how welders are trained. The new generation of welders is being trained not just in torch control, but in data literacy. Training centers and universities are adopting Xiris camera systems to give students a clearer view of the weld pool dynamics and teach them how to interpret digital data in real time. High-speed, high-contrast video analysis enables instructors to explain key principles of heat distribution, metal transfer, and defect formation in ways that traditional observation never could. Research and industry programs are integrating:
As welding evolves into a data-intensive profession, knowledge of digital monitoring tools is becoming as fundamental as manual technique (PTT Institute, 2025). The future of welding monitoring is multi-layered and multidisciplinary: ✔ Real-time systems are becoming standard, not optional (Market Growth Reports, 2025). And driving much of this evolution are companies like Xiris, whose technologies make the invisible visible, turning welding into a measurable, controllable, and improvable process.
ReferencesKim, J., Park, H., & Choi, S. (2024). Deep-learning-based defect detection in real-time welding monitoring. Journal of Welding and Joining, 42(3), 145–158. https://www.e-jwj.org/journal/view.php?number=2032344 Li, Y., & Zhang, P. (2021). Research and prospect of welding monitoring technology based on machine vision. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352328960 Machine Design. (2025). Robotic welding technologies: What’s possible now and what’s ahead. https://www.machinedesign.com/markets/robotics/article/55288120 Market Growth Reports. (2025). Real-time welding monitoring system market report 2025–2035. https://www.marketgrowthreports.com/market-reports/real-time-welding-monitoring-system-market-104369 Motoman. (2025). Top 5 unique trends to watch in robotic welding. https://www.motoman.com/en-us/about/blog/top-5-unique-trends-to-watch-in-robotic-welding Polish Academy of Sciences. (2024). Hybrid monitoring systems in intelligent welding processes. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 69(2), 233–242. https://journals.pan.pl/Content/133809 PTT Institute. (2025). The future of welding courses: Technologies to watch in 2025. https://ptt.edu/the-future-of-welding-courses-technologies-to-watch-in-2025 Quality Magazine. (2024). Application of high-speed machine vision in industrial inspection: Capabilities and future trends. https://www.qualitymag.com/articles/98719 RSI (The Refrigeration School). (2025). The potential of AI in welding in 2025 and beyond. https://www.rsi.edu/blog/welding/the-potential-of-ai-in-welding-in-2025-and-beyond Wikipedia. (2025). Digital twin. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_twin |



.png)

.png)